Laparoscopic Gallbladder Surgery (Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy) is one of the methods used for gallbladder surgery. It is performed on patients who require surgery due to gallbladder problems and involves smaller incisions compared to open surgery. This results in smaller scars, less pain, and shortens the patient’s hospital stay, thereby speeding up the recovery process.
While Laparoscopic Gallbladder Surgery (Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy) is a safe, effective, and suitable procedure for many patients due to less pain, faster recovery, and quicker return to normal activities, it may not be applicable to all patients requiring gallbladder surgery. For instance, if the patient has adhesions caused by previous abdominal surgeries, the laparoscopic procedure may not be feasible. Even if the surgery begins laparoscopically, it may need to be converted to open surgery.
In cases of severe gallbladder infection, serious liver diseases, if gallbladder cancer is detected, or if the patient has significant heart and lung problems, Laparoscopic Gallbladder Surgery (Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy) may not be possible. The surgeon’s experience is also important in this procedure. Experienced surgeons can safely perform this method in some challenging situations.
For Laparoscopic Gallbladder Surgery (Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy),the patient first consults with the doctor to be informed about the procedure. Afterward, an anesthesia consultation is arranged to inform the patient about the general anesthesia that will be administered during the surgery. Preoperative tests are requested, and the patient is prepared for surgery.
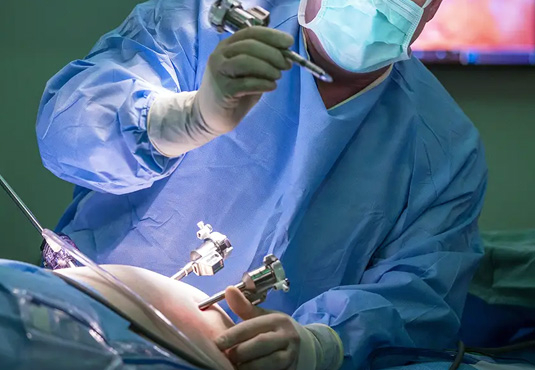
During the surgery, the patient is positioned on their back under general anesthesia. Four small incisions are typically made in the abdomen. To ensure a clear view of the abdominal cavity and allow the surgical instruments to move freely, the abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide gas. Tubes called trocars are placed through these small incisions to facilitate the insertion and removal of surgical instruments.
A camera is inserted through an incision near the belly button to guide the surgeon during the procedure, and the gallbladder is removed through one of the incisions. The abdominal cavity is then inspected, the gas is completely released, and the small incisions are stitched and dressed.
Laparoscopic Gallbladder Surgery (Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy) typically lasts between 40 minutes and 2 hours. The duration can vary depending on the patient’s overall condition, the complexity of the gallbladder problems, any anatomical variations, and the surgeon’s experience. These times do not include preoperative preparation or postoperative recovery.
The cost of Laparoscopic Gallbladder Surgery (Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy) can vary based on several factors. These include the choice of hospital, the surgeon’s experience, and the patient’s health insurance coverage (private health insurance). All of these factors can affect the overall cost of the procedure.
The recovery process following Laparoscopic Gallbladder Surgery (Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy) is usually quick and uncomplicated. Patients can sometimes be discharged on the same day, but most are discharged the next day. After the surgery, patients may experience pain at the incision sites, shoulder pain due to the inflation of the abdomen (which can be managed with simple painkillers),bloating, and gas pains. Following the recommendations of the doctor and dietitian will help make this recovery process smoother.
Simple walking can be started as part of daily physical activities, and further activities should be done based on the doctor's advice. Care of the surgical wounds and follow-up doctor appointments are important. Patients should wait 24–48 hours before bathing, after which they can take showers. Returning to work is generally possible within 1–2 weeks, but those with physically demanding jobs may need to wait 3–4 weeks.
The recovery period after Laparoscopic Gallbladder Surgery (Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy) is typically quick. Patients are usually discharged within 1 day. Most can return to normal daily activities within 1–2 weeks. These timeframes can vary depending on the patient’s overall health, how the surgery went, and whether the patient follows the postoperative recommendations.
During Laparoscopic Gallbladder Surgery (Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy),typically 3–4 small incisions are made. One of these is made around the belly button for the insertion of the camera used during surgery. The other incisions are made on the upper and right side of the abdomen. The number and location of the incisions can vary depending on the surgeon’s preference and the specifics of the surgery.
Laparoscopic surgery (Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy) is the preferred method for gallbladder surgery. It has many advantages over open surgery. Since laparoscopic surgery is performed through small incisions, it results in less scarring, a shorter recovery time, less pain, and a lower risk of infection. For these reasons, the laparoscopic method is a good choice for patients who are suitable candidates for this type of gallbladder surgery.
We are committed to being with you during your treatment process for general surgery diseases with accurate diagnosis and effective treatment methods. Here, you can read the real experiences of my patients who share their health journey with me. Their sincere comments can be a guide for you as well.